The features of 5G currently have the tech world excited about the next frontier of cellular communication. This next step after 4G is increasing speed, performance, and efficiency on enabled devices.
While the benefits of 5G may be obvious, its features, such as faster MIMO, amplified beamforming, URLLC, and high-density support, power its fast adoption by providers.
5G technology will usher in speeds up to 10Gbps on some wavelengths and cut latency periods to about 5ms.
We look at the promises of 5G and why the tech world is in such a frenzy about it.
5G: A Brief Overview
The 5G concept resulted from a 2008 collaboration between NASA and other private parties.
They wanted to develop a communication technology that could improve where other previous communication technologies couldn’t peak.
After several studies by reputable institutions such as New York University, The University of Surrey, and countries such as Israel, India, and Japan, South Korea became the first adopter of 5G.
The U.S. followed. Amid fears and misinformation campaigns, other countries continued to adopt 5G.
Verizon, T-Mobile, and other prominent service providers already have the 5G running.
5G uses the same technology as its predecessors. 3G, 4G, and 4G LTE all use radio waves.
However, the main difference between 5G and the previous generations is the speed, penetration potential, and range of applications.
5G speeds average about 180 Mbps in the U.S. South Korea has the highest average speeds of up to 430 Mbps.
However, 5G has a theoretical potential of 10-20 Gbps. The only limitation to such speeds would be the frequency bands and locations.
5G Core Services
We know 5G has massive speed potential. However, what features enable 5G to be a world changer in communication?
The technology behind 5G is based on three vital services.
Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB)
eMBB is one of three use cases for 5G. It is part of a larger plan to supercharge mobile technology performance.
The basic principle behind eMBB is to enable networks to handle applications and services that need immense speed and high data exchange rates.
Also, eMBB offers a larger area cover compared to 4G. Practical use cases for eMBB include in-vehicle tracking and infotainment, faster real-time streaming, and online 3D 4K resolution gaming.
Evolved phases of 5G-enabled eMCC will cover connected cars and mass-scale autonomous vehicles.
Therefore, we can conclude that eMBB aims to cover three areas to succeed.
- High capacity in heavily populated areas
- Full and enhanced connectivity
- Expanded user mobility
Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications (URLLC)
URLLC is another 5G feature behind mission-critical services. It influences changes in sectors such as factory automation, VR/AR, and the autonomous driving revolution.
It emphasizes the use of low-latency communication and pinpoint accurate reliability.
With the premise of ultra-low latency (-5ms), real-world uses of URLLC are visible in
- Safety and emergency services and response
- Medical services such as remote diagnosis
- Running energy grids
- Powering smart energy operations
Additionally, it also influences the development of faster IoT(Internet of Things) tech. This development guides Tactile Internet, which uses super low latency periods to power human-machine interaction applications.
Massive Machine Type Communications (mMTC)
Interconnectivity in a smart city concept
The Internet of Things and smart tech have two common aspects.
They feature a huge number of devices, and they transmit small packets of data sporadically.
Due to the sheer amount of devices and data, they need a service/technology that can support them to make data flow seamless.
Its proponents designed the service to scale and accommodate additional devices that also carry massive amounts of data that could otherwise congest systems such as 4G.
Also, mMTC is designed to run with little or no human intervention.
What are The Features of 5G?
5G’s services power large-scale communications. However, for these services to run, the features of 5G need to match the premise of 5G.
So here are the vital features to ensure the above services run successfully.
MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output)
MIMO is a data communication feature that enables the exchange of multiple data streams simultaneously. In previous technology (4G and 4G LTE), MIMO supports up to 100 Mbps.
However, 5G can support data streams in the 10-20Gbps range. Yet, 20 Gbps is not even the fastest possible speed. UAE’s Etisalat has breached the 30Gbps barrier in the trial.
5G’s MIMO allows three key things.
Maximum Capacity: Maximum capacity is the data that flows through a communication system to a maximum user count.
Massive MIMO, a 5G principle, is a vital determinant of 5GNR(5G New Radio), a new communication standard that operates on the sub -6 GHz frequency range.
Massive MIMO also ensures that all the users in the communication system get the same resources at the same signal accuracy and time.
Boosted Coverage: The previous generation, 4G, had issues with users not getting equal coverage. The most affected were those in fringe areas where coverage was weak.
However, Massive MiMO offers equal coverage plus 3D beamforming where users can get strong coverage even in far-flung locations.
Under boosted coverage, devices can easily switch to a data stream that’s streaming data when its current one fails or has reduced efficiency.
Better User Experience: Overall, 5G’s MIMO is meant to enhance user experience whether in mobile tech or smart technology. Users can get faster speeds and better coverage with higher data clarity on 5G.
Power Efficiency
You’d expect 5G to consume more power, given its increased capability to send data. However, one of its features is a low-power mode that ensures devices have a quick boot and load time. As a bonus, devices will drain their power slower, maintaining battery life for longer.
High Connectivity Among Devices
5G’s main goal is expanding network capacity to accommodate more users and devices. Lesser networks would strain to cover more devices. However, 5G can accommodate up to a million devices across a square kilometer.
High device connectivity makes room to innovate for smart technology and the Internet of Things.
Beamforming
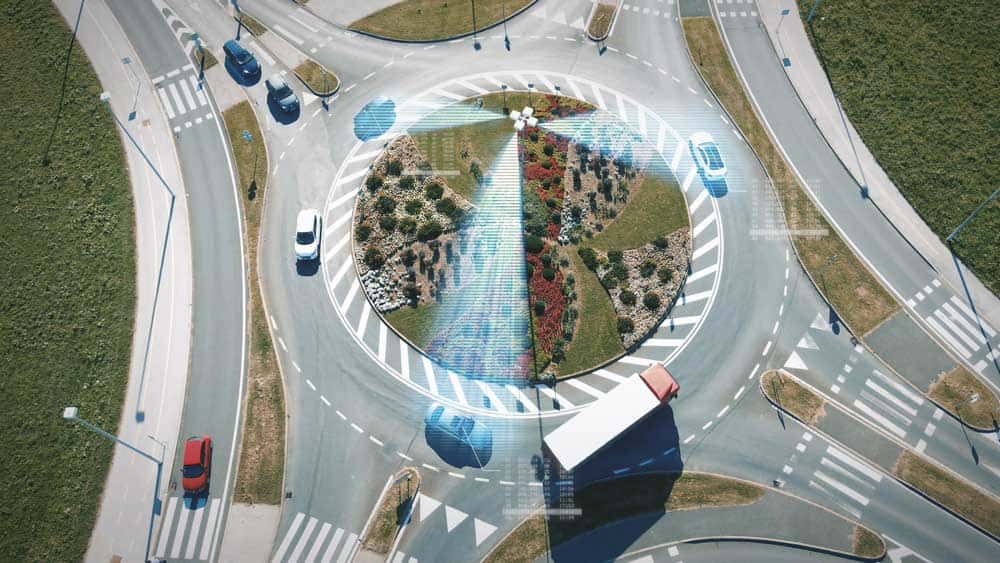

Cell towers supporting 5G technology blasting targeted signals
Signals in cellular technology usually go out in waves. The major design flow in this dispersion method is that some waves get lost in transmission leading to loss of strength and data corruption.
However, think of beamforming as targeted transmission. The transmitter sending data forms a laser beam and targets the waves at a receiver. The result is the receiver gets stronger hyperfocused data packets with minimal loss.
Smaller Towers
Unlike 4G, which has large standalone cell towers occupying large sections of land, 5G utilizes small towers on buildings.
The smaller cell sites are also meant to support more infrastructure to support more devices.
5G travels in three types of waves. The lowest range, the low-band 1 GHz frequency, can travel the farthest. Mid-band 1 GHz-6 GHz frequency waves can travel faster for long distances. Finally, the fastest but weakest waves operate at 24 GHz frequency.
The small but numerous cell sites carry the high-band frequency over long distances to counter the wave’s likelihood of obstruction by tall buildings.
Edge Computing
Edge computing is a 5G feature where applications that process and transit data are built near the generation site.
It enables data to be sent out over shorter distances for less response time.
Conclusion
5G is the result of years of research and studies by many institutions. Although it has faced some criticism over safety concerns, the technology is bound to increase productivity in how we communicate and how we consume data.
The features of 5g are all geared to increase efficiency, speed and user satisfaction.